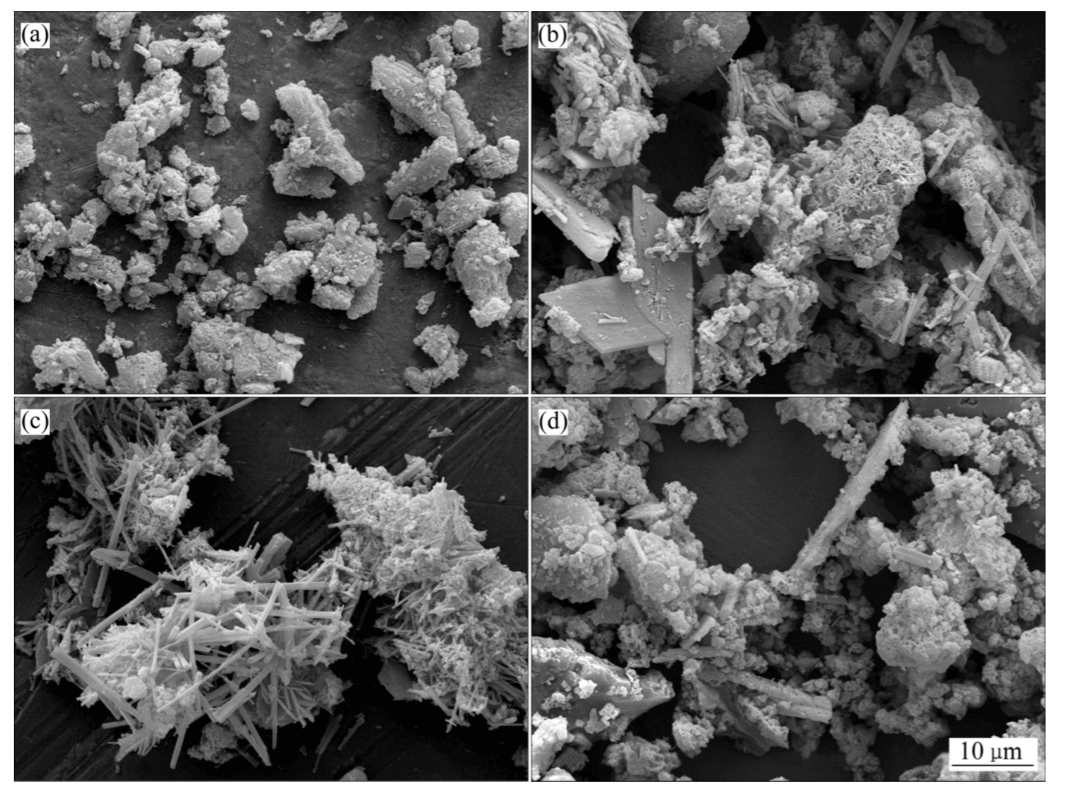
The HDS-CC® (High-Density Sludge Crystal Seed Cycle) process employs recycled high-density sludge from the clarifier to preferentially react with acidic wastewater. Due to its low Zeta potential, the recycled sludge readily adsorbs metal hydroxides, forming initial calcium sulfate nuclei. As the system continuously recirculates, these nuclei grow into granular crystals, achieving efficient solid–liquid separation.

Alkali reagents (Ca(OH)₂, NaOH) are added in stages to precisely adjust pH and remove copper and other heavy metal ions with high efficiency.
A portion of the high-density sludge is recycled back to the neutralization reactor as seed crystals, promoting rapid attachment and growth of new precipitates while minimizing formation of fine flocs.
The ongoing recirculation cycle allows crystals to grow progressively, greatly accelerating settling rates and reducing overall sludge production.
The UltraCav-MBR® system employs high-frequency ultrasonic vibration to induce cavitation in wastewater, generating and collapsing microbubbles that release shock waves and micro-jets. This dual action cleans foulants from the membrane surface—preventing pore blockage—and breaks down macromolecular organics in the sludge into smaller, more biodegradable compounds, reducing membrane fouling. Simultaneously, disruption of microbial flocs releases intracellular substances and enhances biodegradation efficiency. Ultrasonic micro-mixing also intensifies oxygen and substrate transfer, boosting microbial metabolic activity and significantly improving effluent quality.


The AC-DCBS® Activated Carbon Dual-Cycle Bio-coupled System employs a multi-stage “adsorption–coagulation–bioutilization” mechanism for advanced effluent purification. During coagulation, powdered activated carbon and coagulants are added: activated carbon preferentially adsorbs refractory organics and acts as a floc skeleton, while coagulants neutralize colloids to form “activated carbon–aluminum floc” complexes. Flocculants then densify these complexes into rapidly settling flocs. After sedimentation, carbon-laden sludge is split into two recirculation streams: one returns to the coagulation zone to continue adsorption and reduce chemical usage; the other enters an aerobic bioreactor where biofilms degrade adsorbed organics and activated carbon serves as a slow-release carbon source to enhance nitrogen and phosphorus removal. The process achieves synergistic removal via physico-chemical adsorption, chemical coagulation, and biological degradation.


The UVSynOx® UV-Synergized Advanced Oxidation System uses UV photolysis or photocatalysis to activate oxidants (e.g., H₂O₂, persulfates), generating abundant ·OH and SO₄⁻· radicals for rapid mineralization of persistent organics and complex pollutants. The modular system integrates deep detoxification, disinfection, and water quality upgrading, and can be seamlessly combined with membrane filtration or biological processes to tackle high-strength industrial wastewater that resists conventional biological treatment.

